IP Protection in 2019: Cope with Weak Points

Before we investigate familiar techniques of hiding an IP address, a person is to know what his or her IP is. Besides, a man is to find out the things that reveal our devices when connecting to the internet (for example, the IP address of a DNS server). All that is required is to use a service which offers interactive checking of your device through Java, ActiveX, Flash and Javascript.
Some people prefer using Virtual Private Networks others opt for anonymizers. But not all tools cope with the task fair enough. We cover them all with both weak and strong sides.
IP Masking is relevant these days
Elias Heftrig, a worker of the Fraunhofer Institute for Secure Information Technology, has conducted research on Certificate Authorities’ weaknesses. Based on the research findings, 5 out of 17 CAs turned out to be vulnerable to a fragmentation attack of an IP. The result of the investigation was rather surprising for an average user, as IP masking is generally used to be protected when browsing restricted sites and services. But in fact, it goes much deeper than that.
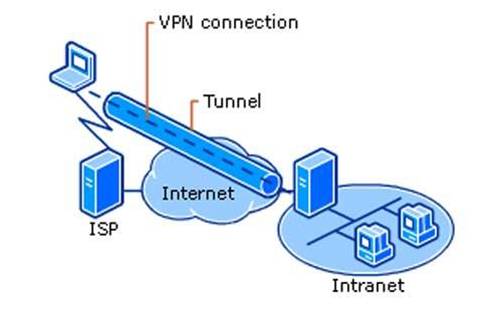
Virtual Private Networks
VPN connection resembles the connection to a local area network: the applications you use will keep on working as usual. When one of them comes to a remote resource, a special GRE-package will be created on a device. Later, it’ll be encrypted and sent to a VPN server. In its turn, this server decrypts the package, identifies the request and makes it on its own behalf. Thus, third-party agencies will see the IP that belongs to a VPN provider but not to a user. The greatest benefit of VPNs (for instance, Trust Zone VPN), is the facility to make use of all their advantageous functions free of charge!
Proxy servers
Proxy is a computer networks service which allows its consumers to make indirect requests to other network services. First, a user connects to a proxy server and requests a resource (for example, a file) located on another server. After it, proxy server connects to the necessary server, gets a resource and delivers it to the client. The IP of a user is masked again. HTTP-proxies are the most commonly used. They are used quite often but work with HTTP only.
Anonymizers
An anonymizer looks like an average search engine with the only difference being that a user should enter a URL instead of a search request. Anonymizers represent scripts in PHP, PERL and CGI. Thanks to anonymizers, ISPs don’t see user’s IP and, therefore, the restricted content becomes unblocked.
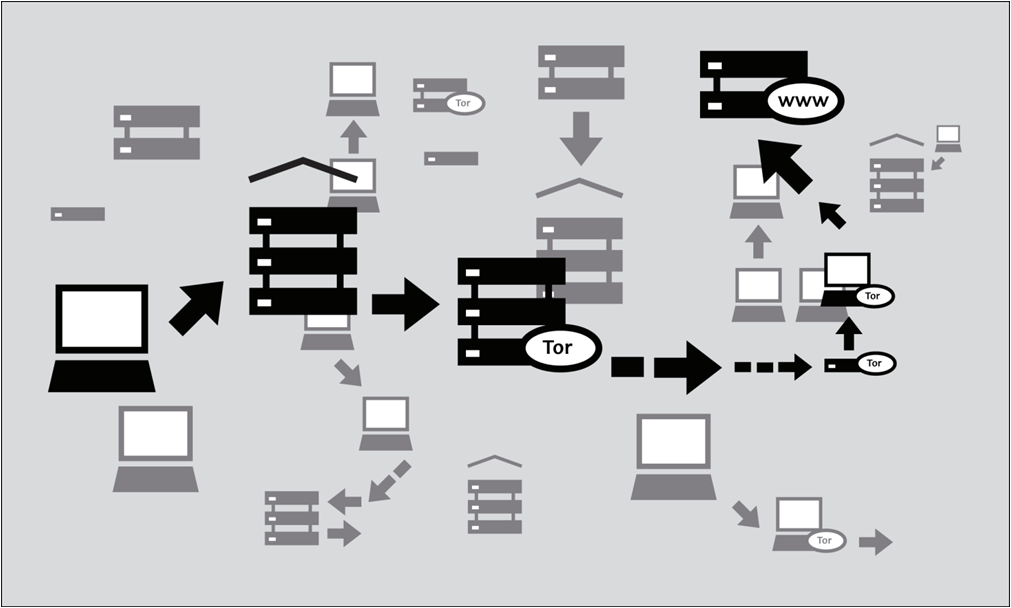
The Onion Router
Tor is a system which allows users to connect to its servers anonymously. Besides, users’ traffic undergoes ciphering when passing through secured nodes. It is typified as an anonymous network which provides unidentified web surfing and safe data transfer. Due to Tor, internet users manage to keep anonymity when accessing websites, publishing information, sending messages, and working with other apps (based on TCP protocol). Traffic protection is provided by means of a wide-area network of servers called onion routers. The users of Tor network enable onion-proxy on their computers, and a virtual chain of free volunteer nodes uses the cryptography for data protection. Everything, including search requests, visited pages and IP, is hidden.
SSH-tunneling
SSH-tunneling is similar to VPN. The operating principle is the following: traffic is forwarded to the assigned port of local hosting. The advantage of this technology is that no additional soft is required to be installed. One will also like the speed – it might become faster. This is due to the fact that traffic undergoes encoding and compressing.
P2P anonymizers
It is a distributed peering network of computers which belong to volunteers all over the world. The network was worked out in order for users to bypass restrictions imposed by local ISPs. As a result, we surf the internet under third-party IP addresses.