The Universal Importance of IAM (Identity and Access Management) In A Firm
The tendency for companies to adopt consumer technologies (also known as commoditization) is increasing rapidly and that means a change in the operation and management of corporate environments and business applications. Organizations have the opportunity to take advantage of these technologies to increase the productivity of their employees and not only the efficiency but also the preservation of productivity of all teams across the board in an organization, especially in work environments that require mobility. This new situation can pose a challenge for IT managers as there is a need for new security policies and access management.
The threats that arise from mobile devices, the cloud, social networks and insecure applications have a determining role in their perception of risk. In addition, the permissiveness in incorporating personal devices in the corporate perimeter (casually known as BYOD – Bring Your Own Device) only aggravates this situation. Since employees use these devices to access corporate resources, organizations must have an Identity and Access Management (IAM) system that simplifies and automates the organization’s setup. The following are the eight best practices to help firms prepare to face this reality:
Audit and control
In a well-designed IAM system, permits are usually assigned to work functions, not to individuals, but permits can be assigned as necessary. Permits require periodic verification and there must be an audit and control process. Organizations need to review who has access to what and determine whether or not they still have the permissions to revoke or provide it on time. It is important to define the work roles within the organization that can certify access rights as well as system owners, administrators and information security managers.
Automate the provisioning of new users
those who leave the organization and those who move – or are promoted or degraded need not to be labor intensive on the part of the IT team. Granting and revoking access rights take a lot of time if carried out through manual methods. Automation can help reduce expenses, reduce human errors and improve consistency.
Provide knowledge and control to business owners
It is critical for the business to be able to answer the question: “Who has access to what, from where, when and how?” The IT manager coordinates the inventory of identities and permits and offers the information to the decision makers as they need it. Allowing data owners to manage access to their data and submit reports and control over permits is presented as a fundamental aspect in good corporate governance. Determine who has access to what data and with what right, since not everyone needs Full access to the system (AKA least privilege concept) is an instrumental ability to protect the corporation against information leaks.
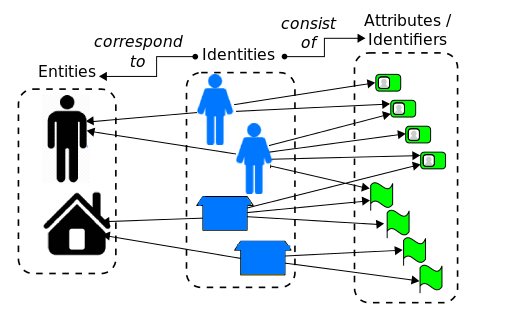
Define the identities
Implement a unique and integrated system that offers complete employee identity management and eliminates orphan identities and phantom accounts that are not needed at the right time. Enterprises usually have a primary directory service, a messaging system, and a resource planning system. All of which must be integrated into the overall identity management architecture in a way that simplifies, automates the operation and identity lifecycle of the firm, including employees access privileges.
Implement processes to manage IT changes
Although the evolution in technology is unstoppable and highly necessary, changes that are not managed can cause problems. The implementation of a workflow of “request and approval” provides an effective way to manage and document the change. It is necessary to have a tool that facilitates the visual creation of these internal processes, integrating with the real business system, taking into account account to all departments and persons of interest.
Provide role-based management
It is necessary that the functions performed by an employee, consequently, the permissions and accesses that he has to the information correspond with the performance of his real work. Therefore, a role-based management (AKA RBAC) allows not assigning rights to people but functions so that if, at some point, another person occupies that role, even temporarily, their access identity can be managed in a simple way and in line with the corporate vision.
Define the universe of employees
Normally, the employees of a firm are managed by the people / human resources department, which, in turn, must manage the information of those who are not employees, such as external providers, most of whom require access to the resources of the company. All this assuming that this management does not belong to a line of business and is outside corporate control. Human resource systems should be used as an authoritative source of data for the IAM system so that a corporation avoids repetitive work, errors, inconsistencies and other problems such as uncontrolled system growth.